The People Paid to Spot Risks See High Chance of ‘Global Catastrophe’ Within 10 Years https://www.cnn.com/2024/01/10/business/wef-global-risks-report/index.htmlHumanity faces a perilous future, marked by an explosion of disinformation turbocharged by artificial intelligence and the devastating effects of climate change.The gloomy outlook comes from an annual survey by the World Economic Forum (WEF) of people paid to identify and manage global risks.
According to the report published Wednesday, nearly two-thirds of respondents expect an “elevated chance of global catastrophes” in the next decade. About 30% expect the same in the next two years.
Over a 10-year horizon, environmental risks including biodiversity loss and critical change to the Earth's systems topped the rankings, with misinformation, disinformation and adverse outcomes of artificial intelligence (AI) just behind.
Bad to WorseResults from the survey “highlight a predominantly negative outlook for the world in the short term that is expected to worsen over the long term,” it added. ----------------------------------------------------------------
Global Risks Report 2024https://www.weforum.org/publications/global-risks-report-2024/digest/https://www.weforum.org/publications/global-risks-report-2024/The Global Risks Report explores some of the most severe risks we may face over the next decade, against a backdrop of rapid technological change, economic uncertainty, a warming planet and conflict. As cooperation comes under pressure, weakened economies and societies may only require the smallest shock to edge past the tipping point of resilience. 2024 Report: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_The_Global_Risks_Report_2024.pdfA deteriorating global outlookLooking back at the events of 2023, plenty of developments captured the attention of people around the world – while others received minimal scrutiny. Vulnerable populations grappled with lethal conflicts, from Sudan to Gaza and Israel, alongside record-breaking heat conditions, drought, wildfires and flooding. Societal discontent was palpable in many countries, with news cycles dominated by polarization, violent protests, riots and strikes. Although globally destabilizing consequences – such as those seen at the initial outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine war or the COVID-19 pandemic – were largely avoided, the longer-term outlook for these developments could bring further global shocks.
As we enter 2024, 2023-2024 GRPS results highlight a predominantly negative outlook for the world over the next two years that is expected to worsen over the next decade (Figure A). Surveyed in September 2023, the majority of respondents (54%) anticipate some instability and a moderate risk of global catastrophes, while another 30% expect even more turbulent conditions. The outlook is markedly more negative over the 10-year time horizon, with nearly two-thirds of respondents expecting a stormy or turbulent outlook.
 Environmental risks could hit the point of no return
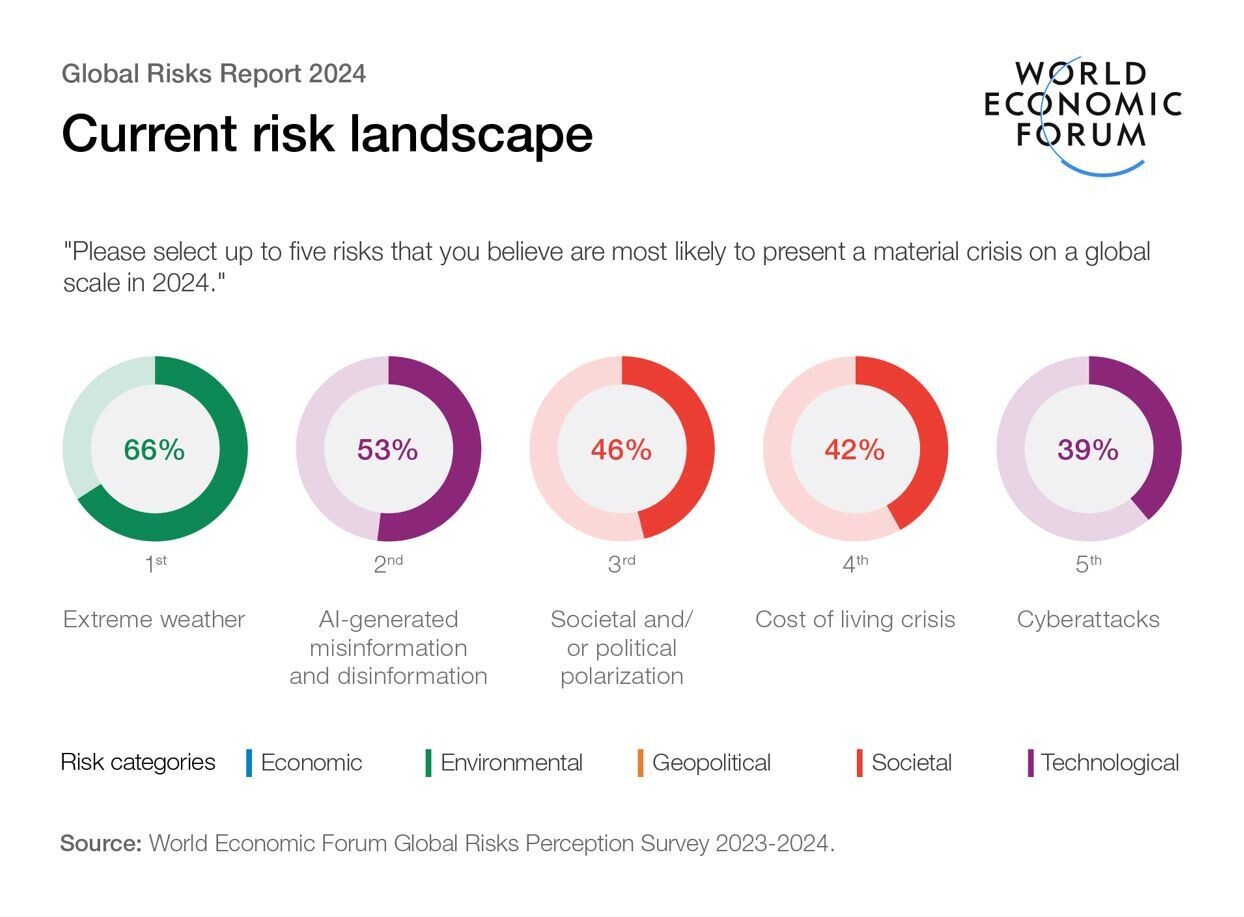
Environmental risks could hit the point of no returnEnvironmental risks continue to dominate the risks landscape over all three time frames. Two-thirds of GRPS respondents rank Extreme weather as the top risk most likely to present a material crisis on a global scale in 2024 (Figure B), with the warming phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle projected to intensify and persist until May this year. It is also seen as the second-most severe risk over the two-year time frame and similar to last year’s rankings, nearly all environmental risks feature among the top 10 over the longer term (Figure C).
 As polarization grows and technological risks remain unchecked, ‘truth’ will come under pressure
As polarization grows and technological risks remain unchecked, ‘truth’ will come under pressureSocietal polarization features among the top three risks over both the current and two-year time horizons, ranking #9 over the longer term. In addition,
Societal polarization and
Economic downturn are seen as the most interconnected – and therefore influential – risks in the global risks network (Figure D), as drivers and possible consequences of numerous risks.

Economic uncertainty will weigh heavily across most markets, but capital will be the costliest for the most vulnerable countries. Climate-vulnerable or conflict-prone countries stand to be increasingly locked out of much-needed digital and physical infrastructure, trade and green investments and related economic opportunities. As the adaptive capacities of these fragile states erodes further, related societal and environmental impacts are amplified.
Similarly, the convergence of technological advances and geopolitical dynamics will likely create a new set of winners and losers across advanced and developing economies alike (Chapter 2.4:
AI in charge). If commercial incentives and geopolitical imperatives, rather than public interest, remain the primary drivers of the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and other frontier technologies, the digital gap between high- and low-income countries will drive a stark disparity in the distribution of related benefits – and risks. Vulnerable countries and communities would be left further behind, digitally isolated from turbocharged AI breakthroughs impacting economic productivity, finance, climate, education and healthcare, as well as related job creation.
Simmering geopolitical tensions combined with technology will drive new security risksAs both a product and driver of state fragility, Interstate armed conflict is a new entrant into the top risk rankings over the two-year horizon (Figure C). As the focus of major powers becomes stretched across multiple fronts, conflict contagion is a key concern (Chapter 1.4: Rise in conflict). There are several frozen conflicts at risk of heating up in the near term, due to spillover threats or growing state fragility.
This becomes an even more worrying risk in the context of recent technological advances. In the absence of concerted collaboration, a globally fragmented approach to regulating frontier technologies is unlikely to prevent the spread of its most dangerous capabilities and, in fact, may encourage proliferation (Chapter 2.4: AI in charge). Over the longer-term, technological advances, including in generative AI, will enable a range of non-state and state actors to access a superhuman breadth of knowledge to conceptualize and develop new tools of disruption and conflict, from malware to biological weapons.
In this environment, the lines between the state, organized crime, private militia and terrorist groups would blur further.
Over the next decade, as dissatisfaction with the continued dominance of the Global North grows, an evolving set of states will seek a more pivotal influence on the global stage across multiple domains, asserting their power in military, technological and economic terms.
As states in the Global South bear the brunt of a changing climate, the aftereffects of pandemic-era crises and geoeconomic rifts between major powers, growing alignment and political alliances within this historically disparate group of countries could increasingly shape security dynamics, including implications for high-stakes hotspots: the Russia-Ukraine war, the Middle East conflict and tensions over Taiwan (Chapter 1.4: Rise in conflict). Coordinated efforts to isolate “rogue” states are likely to be increasingly futile, while international governance and peacekeeping efforts shown to be ineffective at “policing” conflict could be sidelined.
